Emily Newton is a manufacturing and industrial journalist with over 5 years experience covering industry trends. To read more of her work, check out her articles on Revolutionized.
Following the best practices for computer numerical control (CNC) modeling is crucial for keeping costs down and making the overall process as efficient as possible. Here are some helpful tips for helping you improve CNC modeling results.
1. Understand How Your CNC Modeling Software Works
A software title used for CNC machining has various components that bring a design into reality. Knowing how they function will help you see the wide-spanning effects of any design choices made.
For example, the process starts by using a computer-aided design (CAD) tool to create a two- or three-dimensional CNC model. The program allows adding dimension and geometry, plus feature planning.
The design then goes through a computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) tool that extracts the component’s geometrical parameters. The software also creates computerized codes that instruct the CNC machine during its operation.
You’ll typically use software that includes both the CAD and CAM tools packaged together in one program. There are also program features that allow making granular changes to the design. One company saw a nearly 50% rise in CNC machine productivity by utilizing CAD-CAM software.
If you’re working with a software title that’s still unfamiliar to you, take the time to learn your way around the program before accepting any major projects. Doing that will help you make the most of features and avoid mistakes.
2. Consider Requesting Technical Drawings From Clients
A CAD design file programs the CNC machine, but it’s not the only component guiding the process. Your clients may be more satisfied with the results of their CNC designs by submitting technical drawings along with any computerized files.
That’s because a technical drawing can give greater clarity about the CNC model. For example, it may specify a desired surface finish, such as roughness. It can also include sectioned or detailed views that have complex dimensions or internal features.
A technical drawing can serve as a useful reference during the part creation process. Asking clients to provide them before you start on their orders helps ensure you understand and meet their expectations. Since CNC equipment can get machining accuracy within .0001, it’s essential to take care with the design. Technical drawings can help clients better explain what they need and want.
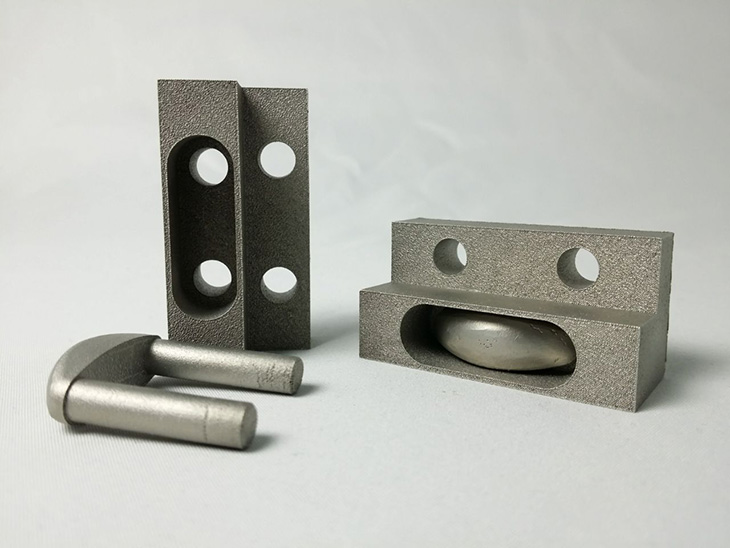
3. Avoid Thin Walls and Small or Unfeasible Features
Certain design features can make your models more or less effective. Some projects will require deviating from best practices. However, keep in mind that it’s best to avoid designing a model with excessively thin walls when possible.
Research shows that lowering the wall thickness also reduces material stiffness. Moreover, certain materials have a minimum requirement for them to function correctly in the finished piece. For example, metal’s minimum thickness is 0.794 millimeters, while plastic’s is 1.5.
Be careful not to design overly tiny features. CNC machines typically have a minimum tool diameter of 2.5 millimeters. Anything smaller than that will add challenges to your CNC design project and prove difficult to machine.
Additionally, you may need to use special tools to create tiny parts, potentially adding to the overall costs of your endeavor. The total machining time becomes the primary cost driver and can affect productivity. When the amount of required work for a single part goes up, expenses do, as well.
Bear in mind that CNC machines cannot create all conceivable parts features. Curved holes are one example. If having such features in the design is essential, designers should plan for using other types of machines to achieve what CNC equipment cannot.
4. See the Link Between Materials and the Overall Results
When designers make CNC models, they must account for a finished part’s desired properties. Must it tolerate exposure to a certain chemical? Does it need thermal stability? Does a particular amount of rigidity affect how the component functions? Considering those things is critical when weighing the pros and cons of available materials. Price specifics should come into play as well, both in terms of the raw costs and machining time.
For example, softer materials like plastic and aluminum machine faster than harder ones. Aluminum is about four times quicker than carbon steel and eight times faster than stainless.
However, designers creating a CNC model must also consider the material blank, which is the piece initially loaded into the machine. A good practice is to ensure it’s at least 0.125 inches larger than the intended size of the part. That’s due to material variations that can cause minor fluctuations.
Additionally, something to keep in mind regarding plastics is that it’s challenging to hold the material to tight tolerances. Relatedly, flexibility could mean the part warps due to stresses placed on it during the CNC machining process or removal from the machine.
Material selection certainly affects how a finished part functions and how much it costs to make. However, the items should also be top-of-mind considerations during the design phase. Your knowledge of how certain materials will perform and the costs associated with them could prove invaluable for helping clients make more informed choices.
Start Improving Your CNC Modeling Skills
It’s unrealistic to hope for perfection when designing any CNC model. However, these four tips will help you steer clear of shortcomings and become more familiar with how seemingly minor design choices can significantly affect the results.